Contraflow Systems - Motorway, Buses, Bikes
Mastering Contraflow Systems: A Complete Guide for Drivers
Mastering Contraflow Systems: A Complete Guide for Drivers
Understanding all the different types of road markings and signs can feel like decoding a secret language—especially when you come across something uncommon like the contraflow system. If your first encounter with it was during theory test revision, you might have thought, “This sounds complicated!” But the good news is: it’s not.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about contraflow systems—what they are, where you’ll find them, how to handle them safely, and what to expect in the theory test.
Whether you’re a week away or the night before your theory test, you’ll walk away with the confidence and clarity to handle any contraflow question that comes your way..

What is a Contraflow System?
What is a Contraflow System?
Let’s start with the name.
"Contra" = against
"Flow" = the direction of traffic
Put them together, and a contraflow system is a road setup where traffic flows against the usual direction on the same carriageway.
Contraflow systems can be either:
Temporary, often set up during roadworks or emergencies
Permanent, such as in towns where buses or cycles are allowed to travel in the opposite direction on one-way streets
Contraflow Systems on Motorways
Contraflow Systems on Motorways
One of the most common places you'll encounter a contraflow as a car driver is on motorways or dual carriageways during major roadworks or closures.
Normally, on a motorway, traffic in each direction is separated by a central reservation—the physical divide that keeps opposing traffic apart.
But what happens when one side of the motorway is closed?
In that case, traffic from the closed side is diverted across the central reservation and onto the opposite carriageway. That means two-way traffic runs side by side, often with just cones separating you from oncoming vehicles.


What Are the Additional Hazards of a Contraflow System?
What Are the Additional Hazards of a Contraflow System?
Contraflow systems can be challenging because they break the usual road conventions we rely on. Here are the key hazards:
🚗 Narrower lanes – Space is tight, and there's less margin for error
↔️ Proximity to oncoming traffic – Only a line of cones between you
🛑 No hard shoulder – Breakdowns become more dangerous
🔩 Debris and obstacles – Higher risk from litter or crash aftermath
🧠 Reduced reaction time – Especially if others make mistakes
How should you drive in a contraflow?
Get into the correct lane early
Stick to your lane—do not overtake
Keep a safe following distance
Watch for lower speed limits
Never cross the cones—even for emergency vehicles
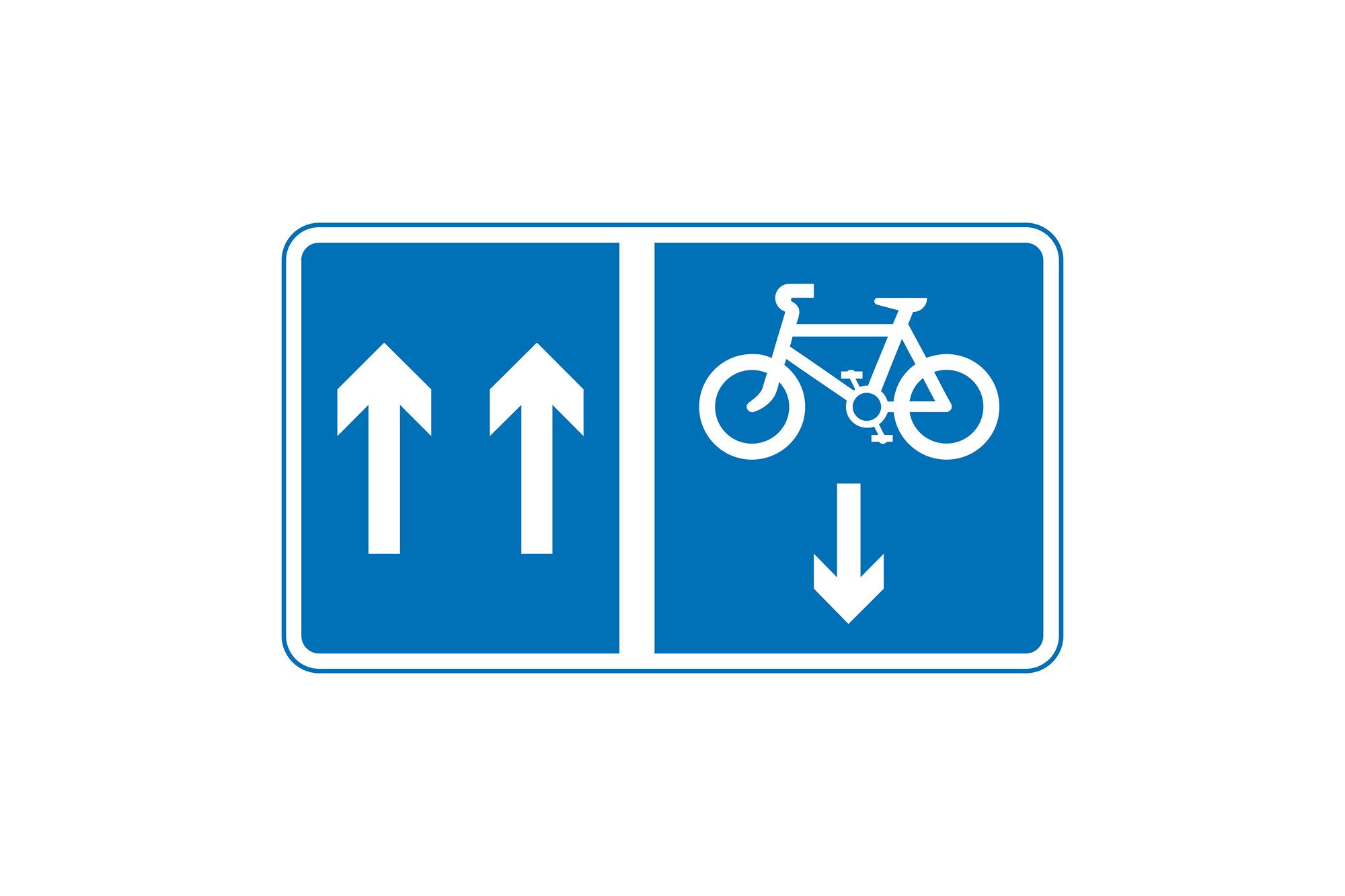
Contraflow Cycle Lanes
Contraflow Cycle Lanes
In urban areas, especially on one-way streets, you might see contraflow cycle lanes. These allow cyclists to travel in the opposite direction to motor traffic—legally and safely.
Why do they exist?
Because one-way systems often disadvantage cyclists, forcing them onto busier roads or into risky shortcuts. Contraflow cycle lanes make it safer and faster for cyclists to get around without endangering pedestrians by riding on the pavement.
Key features:
Marked with blue signs and clear road markings
Solid white line: Do not cross
Dashed white line: Cross only when safe and necessary
Always check for cyclists before turning or pulling out—they may be coming from a direction you wouldn’t normally expect on a one-way street.
Contraflow Bus Lanes
Contraflow Bus Lanes
These work on the same principle as cycle lanes: allowing buses to travel against the general flow of traffic on one-way streets.
Why?
To give public transport a faster, more direct route—helping reduce congestion and improving journey times.
How to spot them:
Look for the contraflow bus lane sign—a blue rectangle with arrows showing opposing traffic, usually with a bus icon on one side.
It's a very common theory test question and easy to miss if you’re not familiar with the sign.
Some contraflow bus lanes are shared with cyclists, so keep your eyes peeled for both users.
With-Flow Bus and Cycle Lanes
With-Flow Bus and Cycle Lanes
If contraflow means against the flow, then with-flow means travelling in the same direction as the surrounding traffic.
These are the more common bus and cycle lanes you're used to seeing, running alongside normal traffic in the same direction.
Signs to watch for:
With-flow lane signs do not have arrows
You must not drive or stop in them during restricted hours
Make sure you can distinguish these from their contraflow counterparts, especially during the theory test.


Contraflow Systems on the Theory Test
Contraflow Systems on the Theory Test
There’s a strong chance the theory test will include a question or two about contraflow systems. Make sure you're confident in the following areas:
✅ What a contraflow system is and where it’s used
✅ What hazards are involved when driving through one
✅ What the signs for contraflow bus and cycle lanes look like
✅ How with-flow lanes are different
✅ What happens to speed limits and lane widths in motorway contraflows
✅ What behaviour is expected from drivers—especially regarding overtaking, lane discipline, and emergency vehicles
Contraflow Systems Explained
Final Thoughts: Respect the Flow
Contraflow systems aren’t designed to catch you out. They exist to keep traffic moving safely and efficiently—even in tricky conditions like roadworks or city congestion.
Learn the signs. Respect the rules. And always stay calm and aware—whether you’re on the road or sitting the test.
By knowing the difference between contraflow and with-flow systems, you’re not just preparing for the theory test—you’re building the habits of a safe, competent driver for life.

